2.2
Preoperative examination
Preoperative examination Preoperative examination Preoperative examination Preoperative examination Preoperative examination Preoperative examination Preoperative examination
Preoperative examination includes:
- general examination (patients’ complaints related to the necessity of dental implantation; anamnesis; blood test (complete blood count, coagulation test, Wassermann test, HIV test, hepatitis test). A patient’s medical condition may require additional examinations (biochemical blood test, blood glucose test) or a physician’s consultation on the possibility of a dental implantation.
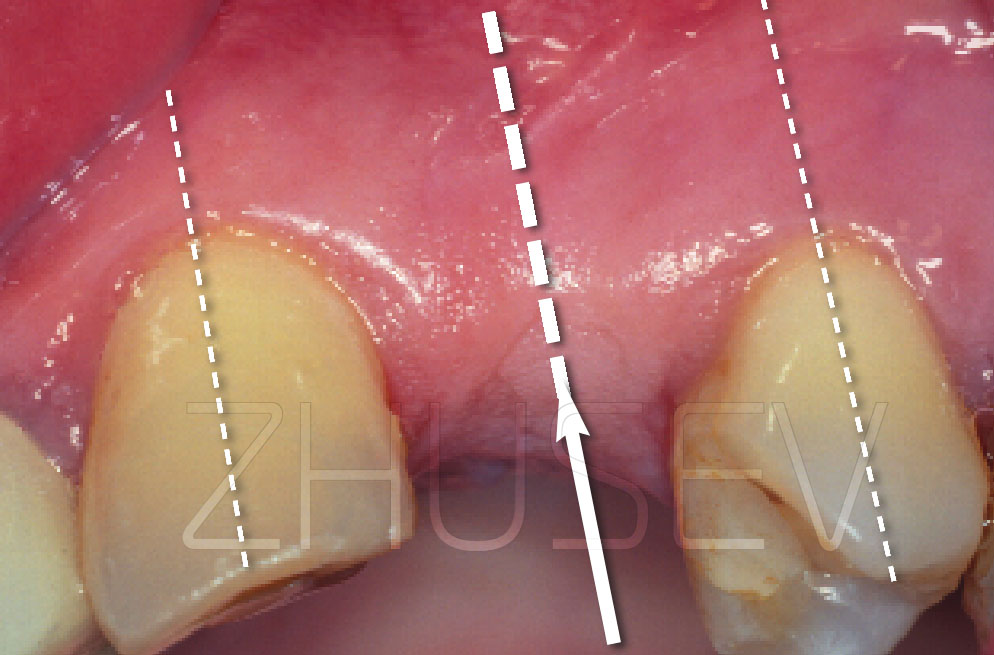
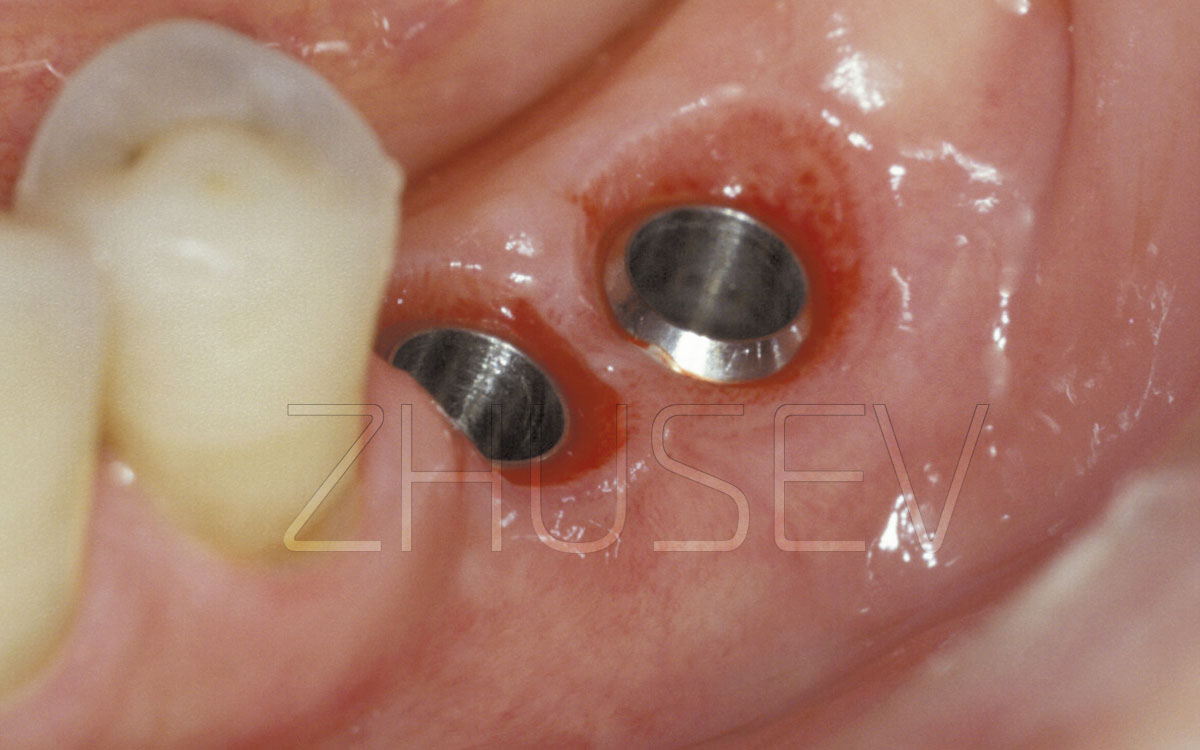
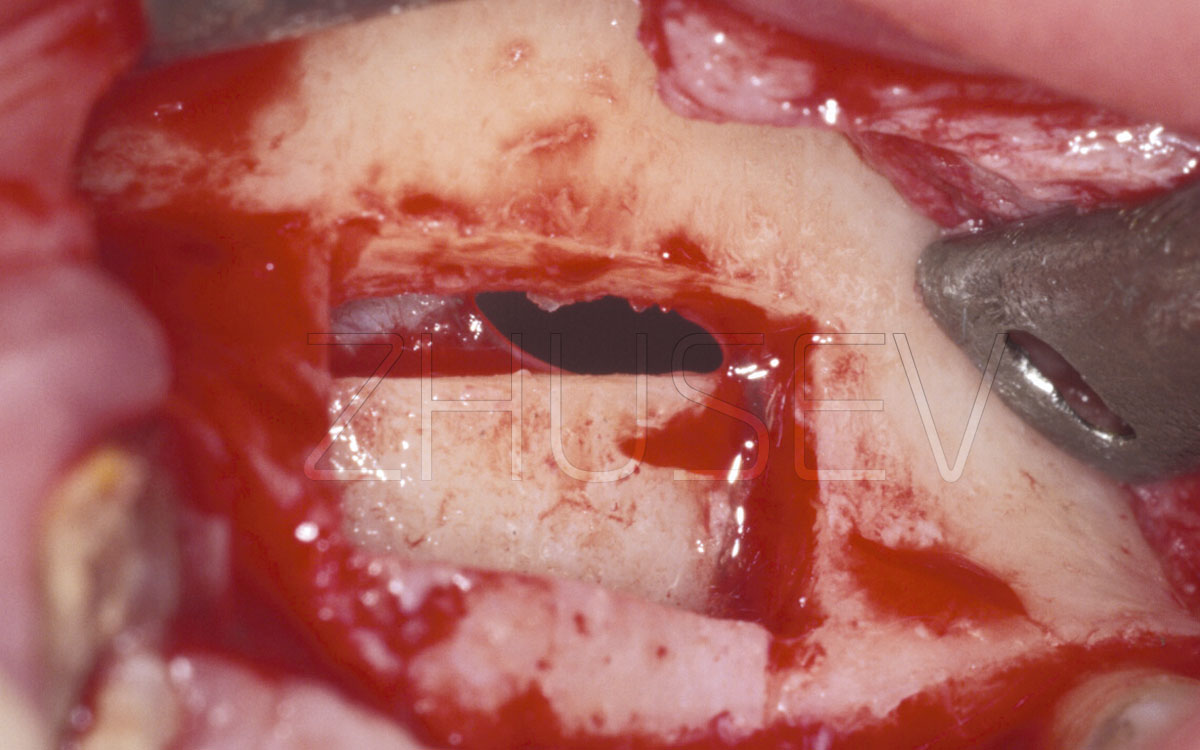
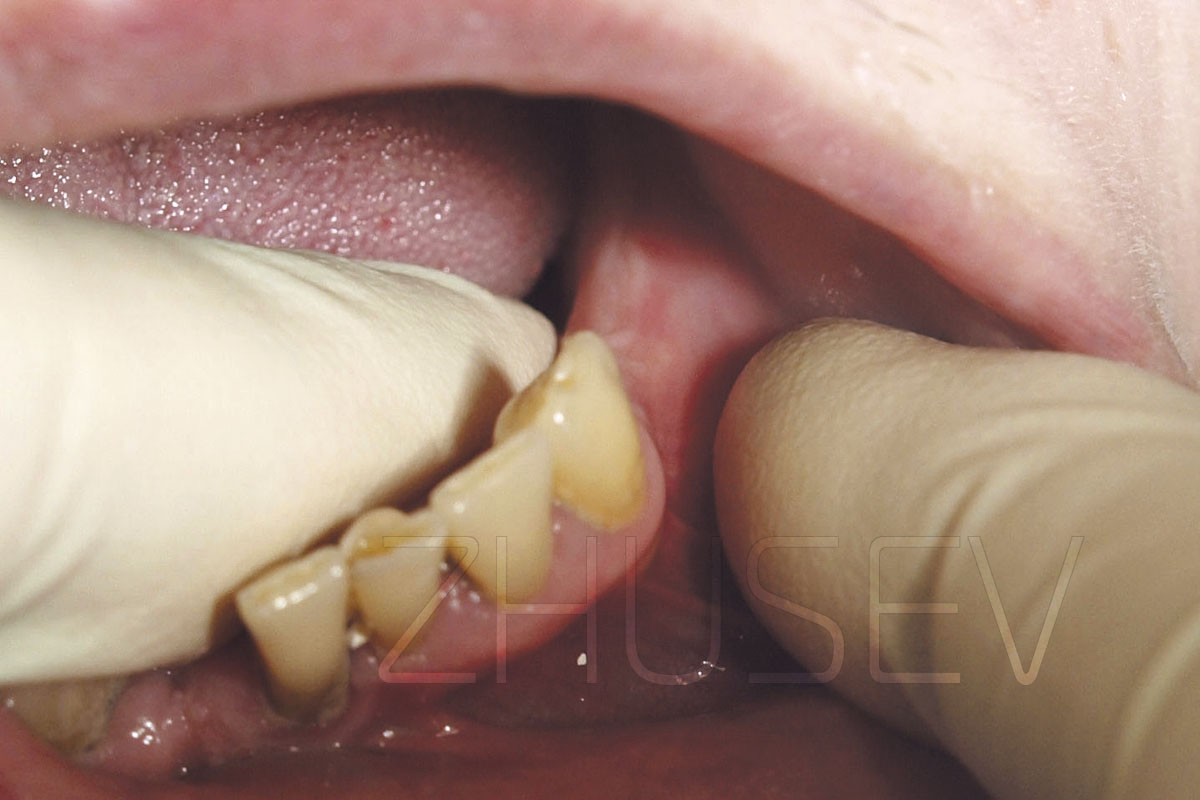
- dental examination (dental health, periodontal status of teeth adjacent to proposed implant sites, periodontal status of the abutment teeth, periodontal status of dental antagonists; the quality of dental restorations, mucosal condition of the oral cavity, severity of alveolar ridge atrophy, interarch distance, or interalveolar space (if the available space is less than 7 mm or greater than 14 mm, additional surgical procedures and more complex prosthetic procedures are required).
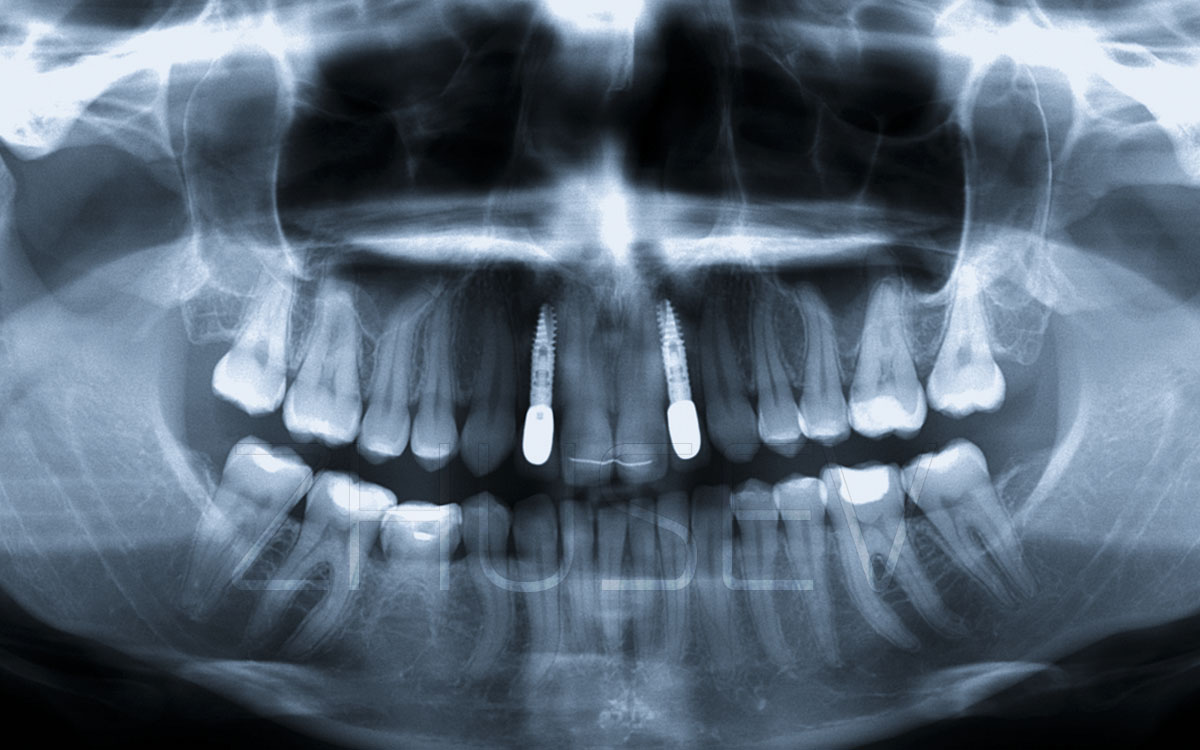
- X-ray examination (normally: an orthopantomogram and a focal spot radiograph of the proposed implant site).
Magnetic resonance imaging is certainly the most informative, but it is really necessary only in complex or dubious cases.