There are several classifications of dental implants based on various principles. The most widely spread classification is based on the position of an implant relating to the surrounding tissues. According to the classification dental implants are subdivided into:
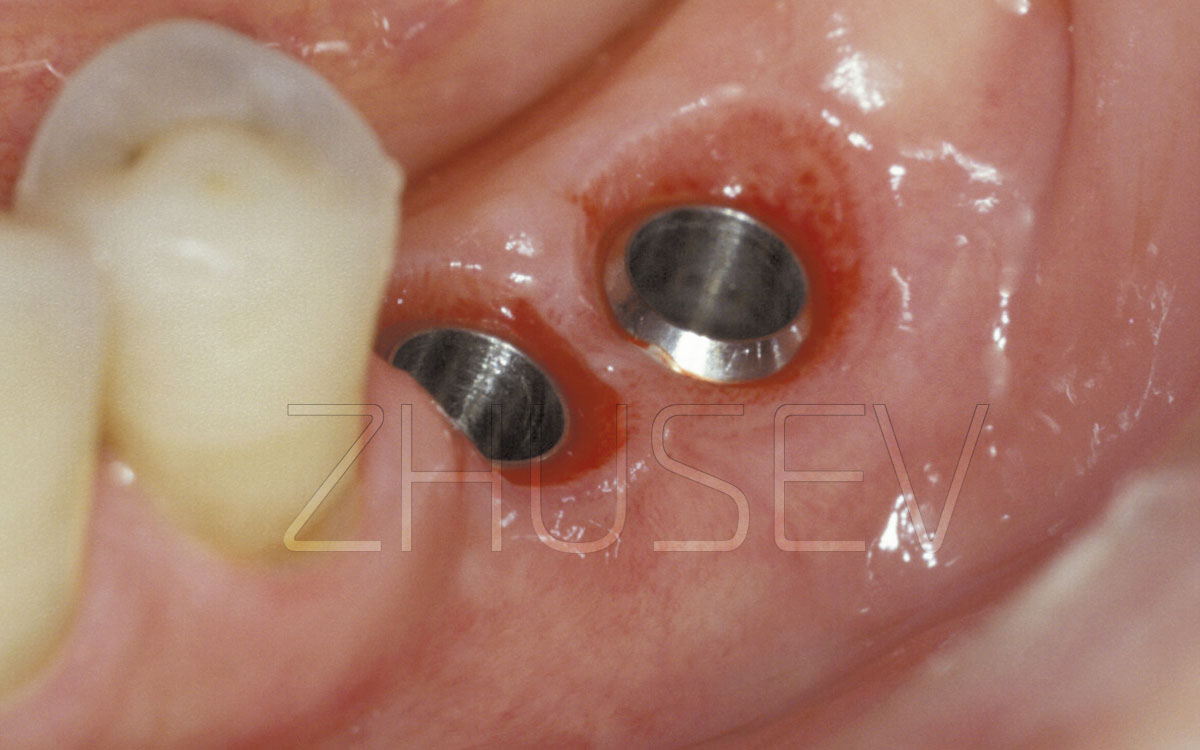
Endosseous implants are most widely spread, for they guarantee long-term stable aesthetic and functional results. According to statistics collected within a ten-year period, about 88 – 96 % of endosseous implants (there are various shapes) perform well.
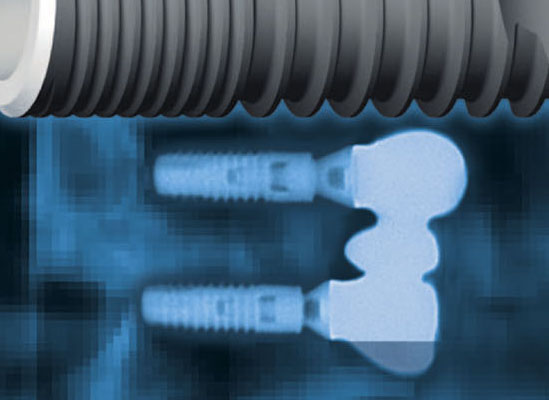
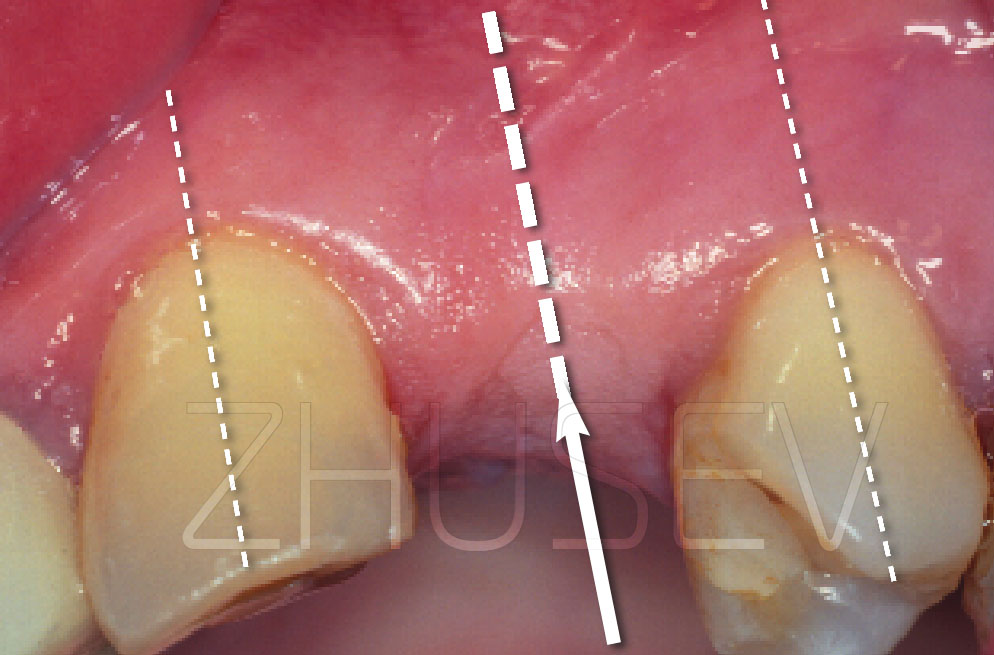
Endosseous implants have the following components 1.2.1 A-D:
Many “Bone Level” implants, which are totally embedded in jawbone and do not show above the gum line, have no transgingival components 1.2.1 C,D.
According to their construction, dental implants can be:
Non-demountable 1.2.1 B. In this case, an abutment and an endosseous dental implant body form an integral whole. If repositioning of a dental implant abutment is required, the abutment is either removed or bent.
Demountable 1.2.1 C. In this case, an implant can be used together with a variety of abutments, which secures optimal positioning of the final restoration and can be used with a variety of constructions, enabling replacement.